Multi-Factor Authentication: What it is and why you should use it
Updated August 30, 2024 | Published October 17, 2023 by Angela Talbot
-
Categories:
- Security & Fraud Prevention

When it comes to protecting your personal information, Multi-Factor Authentication, or MFA, is an extra layer of security that will make it harder for cybercriminals to access your online accounts.
The last thing anyone wants is for a stranger to gain access to accounts where they can find personal, banking, or medical information. Recovering from a breach can cause tremendous stress. Using multi-factor authentication can save you from that headache by adding login requirements that are too complicated for a cybercriminal to figure out.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication?
MFA adds a second or even third layer of protection to your accounts in order to identify that it’s you who is logging in. It means you have additional verification steps to complete after you’ve typed in your username and password. So, if a cybercriminal has your login information, they will be stopped once they reach this point. Some cloud-based services will enroll you in MFA automatically when you first sign up.
The three categories of authentication factors
- Something you know
- Knowledge factors are things like passwords, PINs, or security questions (like: What town did you grow up in?)
- Something you have
- Possession factors are things you own, such as your mobile phone, key fobs, or smartcards.
- Something you are
- These are inherence factors or biometrics that are your own unique physical traits. Such as: thumbprint, facial recognition, voice recognition, or retinal scans.
How Multi-Factor Authentication works
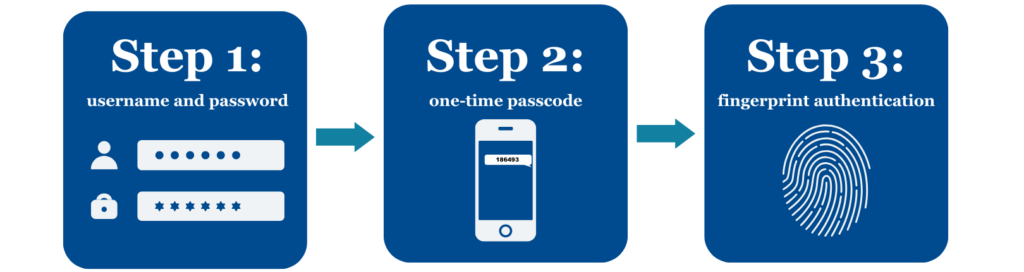
Scenario: after you type your username and password, a one-time passcode will be sent to your phone via text. Sometimes a passcode will be sent to your email, but typically, the phone is a safer option as it is more unlikely for a cybercriminal to have access to it. Only you can see that code and it will only work for a certain amount of time (usually between 10-30 minutes). Once you type in the passcode, you may need to complete a fingerprint scan as a final step.
There are many combinations of the three factors that you could have to identify yourself. This is just one example. The added layer ensures that even if someone has stolen your password, they would need additional information or items to access your account.
Why you should use Multi-Factor Authentication
Security questions alone sometimes don’t cut it anymore. If you’re not careful with the information you put online, a fraudster could find the answers to those questions and log in as you. Adversaries seeking your personal information are persistent and may employ brute force attacks to crack even the strongest passwords.
Security breach alerts
If you receive a one-time passcode to your phone when you were not trying to log in, you will know someone has gained access to your username and password. This serves as an early warning system, indicating possible unauthorized attempts to access your account. Luckily, they were stopped at the next step, but you should immediately change your password for that account.
Safe banking online
Webster First online banking uses MFA to keep your accounts safe. You’ll be prompted to enroll when you first set up online banking. If you are already signed up and need to change your verified device, click on “My Settings” and then “Security options.”
The security of your accounts is very important to us. To provide added protection, our online banking platform is compatible with Google and Microsoft authenticator apps. You can download these apps from the Google Play Store or the App Store.
For more resources on cybersecurity, see: